CDL Practice Tests: Flatbed Cargo Securement
Choose A Section:
Go!The definition for "shortwood" identifies pieces that are no longer than:
- The width of the road.
- 16 ft
- Half the length of the trailer.
- 75 in
Shortwood
- Normally up to about 2.5 m (100 in) in length.
- No longer than 4.9 m (16 ft) in length.
-
Also called:
- Cut-up logs
- Cut-to-length logs
- Bolts
- Pulpwood
To satisfy general cargo securement requirements, what is the minimum WLL for securing vehicles under 10,000 lbs?
- 30% of the weight of the cargo.
- 50% of the weight of the cargo.
- 10,000 lbs.
- 4,500 lbs.
Note: More tiedowns may be required to satisfy the general cargo securement requirements. The Standard states: "The sum of the working load limits from all tiedowns must be at least 50% of the weight of the cargo."
The aggregate WLL for logs loaded lengthwise must be at least:
- 1/2 the weight of the load.
- 1/2 the weight of the stack.
- 1/6 the weight of the stack.
- 4,000 lbs
Working load limit for longwood and shortwood loaded lengthwise
The aggregate working load limit for all tiedowns must be no less than 1/6 the weight of the stack of logs.
Note: This requirement is much less than the general requirement of an aggregate working load limit equal to 1/2 the weight of the load. This lowered requirement recognizes that the bunks/stakes help to prevent slippage.
Concrete pipe loaded crosswise generally:
- At least one tiedown through the rear pipe of the bottom tier must run forward at an angle not more than 45 with the horizontal when viewed from the side of the vehicle, when ever practical.
- Concrete pipe with an inside diameter up to 1.143 m (45 in) can form a complete single tier on a typical flatbed vehicle. Larger pipe often can only be carried as a partial tier.
- All of these things apply.
- Note: At least one tiedown through the front pipe of the bottom tier must run rearward at an angle not more than 45 with the horizontal when viewed from the side of the vehicle, when ever practical.
Special Circumstances: Securing Pipe with an Inside Diameter Up to 1.143 mm (45 in)
Concrete pipe with an inside diameter up to 1.143 m (45 in) can form a complete single tier on a typical flatbed vehicle. Larger pipe often can only be carried as a partial tier.
Note: This pipe diameter of 1.143 m (45 in) is simply a convenient breaking point between "medium" and "large" diameter pipe.
Note: At least one tiedown through the front pipe of the bottom tier must run rearward at an angle not more than 45 with the horizontal when viewed from the side of the vehicle, when ever practical.
At least one tiedown through the rear pipe of the bottom tier must run forward at an angle not more than 45 with the horizontal when viewed from the side of the vehicle, when ever practical.
To secure paper rolls with eyes horizontal against rearward movement, you can use which of the following except:
- The vehicle wall.
- Friction mats.
- Other cargo.
- Blocking.
Direction of Potential Movement: Rearward
Methods to Prevent Movement:
- Other cargo
- Blocking
- Fiction mats
- Tiedowns
What is a cab shield?
- A vertical barrier across the front of the deck of a vehicle to prevent forward movement of cargo.
- A structure, device, or another substantial article placed against or around an article to prevent horizontal movement of the article.
- A vertical barrier placed directly behind the cab of a tractor to protect the cab in the event cargo should shift forward.
- The depression formed between two cylindrical articles when they are laid with their eyes horizontal and parallel against each other.
When securing concrete pipe up to 45 inches loaded crosswise, tiedowns through the pipe must be:
- Wire.
- Chains
- Straps.
- Nylon rope.
Tiedown requirements
- Pipe may be secured individually or as a group.
- Tiedowns through the pipe must be chains.
- Front-to-back tiedowns may be chain or wire rope.
When securing paper rolls with eyes crosswise, which of the following can be used to prevent side-to-side shifting when there is more than 8 inches of space to the wall?
- Friction mats.
- Void fillers.
- Tiedowns.
- Any of these methods are acceptable.
Requirements for eyes crosswise: prevent rolls from shifting toward either wall
If there is more than a total of 203 mm (8 in) of space between the ends of a paper roll and other rolls or the walls of the vehicle, use one of these methods:
- Void fillers (such as honeycomb)
- Blocking
- Bracing
- Friction mats
- Tiedowns
When securing a non-cubic boulder with an unstable base, the four surrounding chains must have a WLL of at least:
- 5,000 lbs
- 50% the weight of the boulder
- 11,000 lbs
- 25% the weight of the boulder
Special Circumstances: Securing a Non-Cubic Shaped Boulder with an Unstable Base
The securement of a non-cubic shaped boulder with an unstable base must meet these requirements in addition to the other large boulder requirements in Section 13.

Surround the top of each boulder at a point between 1/2 and 2/3 of its height with one chain.
The WLL of the chain must be at least 50% of the weight of the boulder.
Attach four chains to the surrounding chain and the vehicle to form a blocking mechanism that prevents any horizontal movement.
Each chain must have a WLL of at least 25% the weight of the boulder, and the angle of the chain must be less than 45° from the horizontal.
Requirements for securing a non-cubic shaped boulder with a stable base include all of the following except:
- Secure each boulder individually with at least two chain tiedowns forming an X pattern over the boulder.
- Pass the tiedowns over the center of the boulder
- Attach chains together at the intersection
- Wrap chains around the circumference of the boulder.

Secure each boulder individually with at least two chain tiedowns forming an X pattern over the boulder.
Pass the tiedowns over the center of the boulder and attach them to each other at the intersection by a shackle or other connecting device.
About The Flatbed Cargo Securement CDL Manual
Studying the flatbed cargo securement CDL manual is not a requirement for getting your CDL permit or license. It is required knowledge for flatbed drivers.
Some questions you should be able to answer for flatbed cargo securement:
- What is the minimum Working Load Limit of a tiedown used to secure logs?
- What is the minimum weight of a shipment of paper rolls that would require specific securement requirements?
- When securing concrete pipe over 45 inches loaded crosswise, which direction must the tiedowns on the front half of the load run?
- What is a cab shield?
- When securing concrete pipe over 45 inches loaded crosswise, which direction must the tiedowns on the rear half of the load run?
- What is a dunnage bag?
- Who is responsible for inspecting securing devices and cargo within the first 50 miles?
- How many tiedowns are required on a stack of shortwood loaded crosswise?
- What is the minimum working load limit of each tiedown used to secure crushed or flattened vehicles?
- Define 'bolster'
- What is a hook-lift container?
- When a tiedown is attached directly to the cargo, what is the ideal angle where it attached to the vehicle?
What is a securing device?
Any device specifically manufactured to attach or secure cargo to a vehicle or trailer:
- Synthetic Webbing
- Chain
- Wire rope
- Manila rope
- Synthetic rope
- Steel strapping
- Clamps and latches
- Blocking
- Front-end structure
- Grab hooks
- Binders
- Shackles
- Winches
- Stake pockets
- D-rings
- Webbing ratchet
- Bracing
- Friction mat
What is a tiedown?
A combination of securing devices that forms an assembly that:
- Attaches cargo to, or restrains cargo on a vehicle.
- Is attached to anchor point(s).
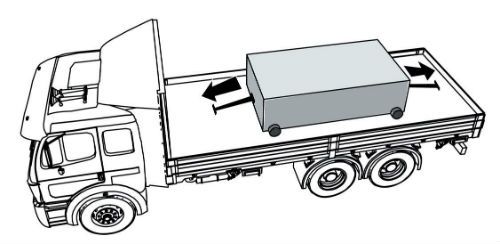
Some tiedowns are attached to the cargo and provide direct resistance to restrain the cargo from movement.
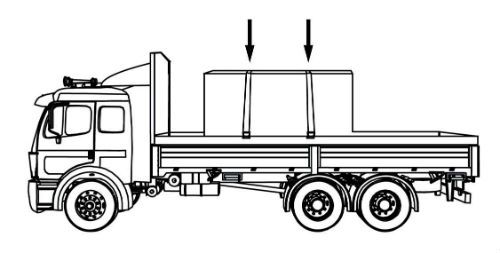
Some tie-downs pass over or through the cargo. They create a downward force that increases the effect of friction between the cargo and the deck. This friction restrains the cargo.
 Related Cargo Securement Terms That Every Driver Should Know:
Related Cargo Securement Terms That Every Driver Should Know:
-
Tiedown:
A combination of securing devices which form an assembly that attaches cargo to, or restrains cargo on, a vehicle or trailer, and is attached to anchor point(s).
-
Contained:
Cargo is contained if it fills a sided vehicle, and every article is in contact with or sufficiently close to a wall or other articles so that it cannot shift or tip if those other articles are also unable to shift or tip.
-
Blocking:
A structure, device, or another substantial article placed against or around an article to prevent horizontal movement of the article.
How should tiedowns be attached?
Tiedowns can be used in two ways:
-
Attached to the cargo:
- Tiedowns attached to the vehicle and attached to the cargo.
- Tiedowns attached to the vehicle, pass through or aroundan article of cargo, and then are attached to the vehicle again.
-
Pass over the cargo:
- Tiedowns attached to the vehicle, passed over the cargo, and then attached to the vehicle again.
Tiedown placement:
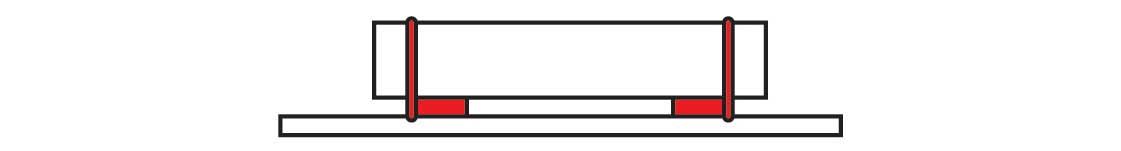
Place the tiedown as close as possible to the spacer.
Position the tiedowns as symetrically as possible over the length of the article.
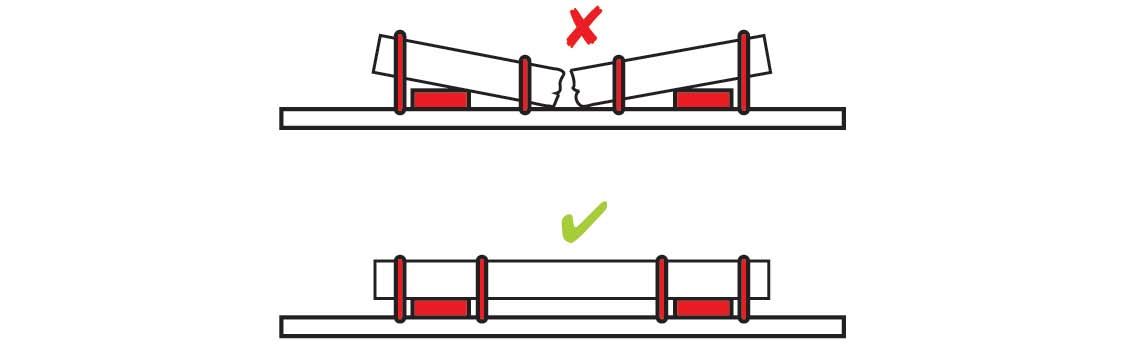
Position the tiedowns to preserve the integrity of the article.




 TT On Facebook
TT On Facebook