CDL Practice Tests: Weight & Balance
Choose A Section:
Go!What are the Federal standards for the gross vehicle weight of a 5 axle commercial vehicle?
- 80,000 pounds
- 22,000 pounds
- 60,000 pounds
- 65,000 pounds
- 20,000 pounds single axle weight
- 34,000 pounds tandem axle weight
- 80,000 pounds gross vehicle weight
- Bridge Formula Calculations
If you are able to exert 200 pounds of force against an object but you are only exerting 50 pounds of force to do so, what method are you applying to make this happen?
- Momentum
- Leverage
- Center of gravity
- Centrifugal Force
You weigh the truck immediately before and after fueling. Based on the following, determine what percentage of the weight goes to each set of axles:
steer: 11,450, drives: 33,100, gross: 76,700
After fueling:
steer:11,850, drives: 33,300, gross: 77,300
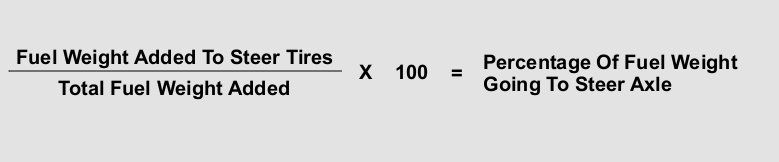
- 75% went on the steer axle
25% went on the drive axles - 88% went on the steer axle
12% went on the drive axles - 67% went on the steer axle
33% went on the drive axles - 73% went on the steer axle
27% went on the drive axles
400/600 = .67
.67 * 100 = 67% fuel weight to the steer tires
100% - 67% = 33% went on the drive axles.
What is the main factor affecting the low-speed offtracking of a tractor trailer?
- The distance from the trailer kingpin to the center of the trailer rear axle
- The length of the trailer, regardless of the position of the trailer tandems
- The distance from the steer axle to the drive axles
- The ratio of the length of the tractor to the length of the trailer
When a combination vehicle makes a low-speed turn - for example a 90-degree turn at an intersection - the wheels of the rearmost trailer axle follow a path several feet inside the path of the tractor steering axle. This is called low-speed offtracking. Excessive low-speed offtracking may make it necessary for the driver to swing wide into adjacent lanes to execute the turn (that is, to avoid climbing the inside curbs or striking fixed objects like telephone poles).
This performance attribute is affected primarily by the distance from the trailer kingpin to the center of the trailer rear axle, otherwise known as the wheelbase of the semitrailer. To prevent trucks from being too long to maneuvering safely around turns encountered in cities and towns, the maximum length allowed from the kingpin to the trailer tandems is set by the individual states.
Based on the following figures, how much fuel can you legally add while remaining legal on the drive axles?
Weight Before Fueling: Steer: 11,275, drives: 33,750, gross: 77,220
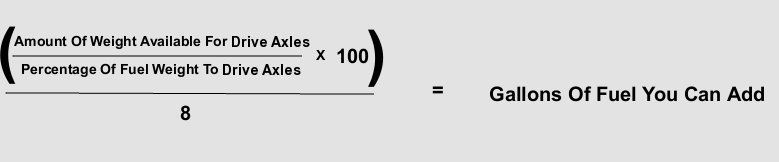
- 110 gallons of fuel
- 104.13 gallons of fuel
- 112.75 gallons of fuel
- 88.5 gallons of fuel
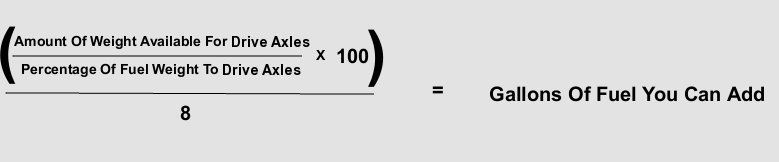
250/30 = 8.33
8.33x100 = 833
833/8 = 104.13 gallons of fuel you can add
Using 6 miles per gallon as your fuel mileage and 8 pounds per gallon for the weight of fuel, how much total fuel weight will you burn off in 600 miles?
- 480 pounds of fuel
- 800 pounds of fuel
- 600 pounds of fuel
- 850 pounds of fuel
Number of miles travelled / miles per gallon = gallons of fuel burned off
100 gallons x 8 pounds per gallon = 800 pounds of fuel burned off
What are the two most common tandem slider rail hole spacings, and roughly how much weight is transferred per hole?
- 4 inches apart - 250 pounds per hole
6 inches apart - 400 pounds per hole - 6 inches apart - 250 pounds per hole
10 inches apart - 500 pounds per hole - 4 inches apart - 450 pounds per hole
6 inches apart - 200 pounds per hole - 6 inches apart - 350 pounds per hole
8 inches apart - 550 pounds per hole
Sliding your trailer tandems forward or backward will redistribute the weight mainly between which two sets of axles?
- Steer axle and trailer tandems
- Drive axles and trailer tandems
- Steer axle and drive axles
- None of these answers are correct
What is the best way to determine what percentage of the weight of fuel will go to each set of axles?
- Weigh the truck immediately before and after fueling, and do a simple calculation
- The percentage is standardized amongst manufacturers and is the same for every truck
- Simply go by the number of gallons of fuel each tank holds
- Ask another driver what their numbers are
What is the cargo's center of gravity?
- The center point of the cargo's weight.
- The average height of the cargo above the trailer floor.
- The distance from the front of the trailer to the center point of the cargo.
- The overall length of the cargo after being loaded into the trailer.
About The Weight And Balance Section
This section was created by Trucking Truth to help people understand how to load cargo, scale the truck, and understand the laws about truck weight limits. These materials will not be on your written CDL exams but it is critical that every truck driver knows these materials.
Types Of Weight Limits
There are four basic weight limits: single axle, tandem axle, bridge formula, and gross vehicle. The Federal Standards are as follows:
- 20,000 pounds single axle weight
- 34,000 pounds tandem axle weight
- 80,000 pounds gross vehicle weight
- Bridge Formula Calculations
Why Do These Different Weight Limits Exist?
There are a long list of critical safety issues which require putting limitations on the gross weight, axle weights, the weight distribution across the length of a vehicle, and the weight distribution across a minimum number of axles.
- Putting too much weight on a small area of the road surface can cause ruts, cracks, and potholes
- Putting too much weight on a small area of a bridge surface can cause structural damage to the bridge
- Too much weight on your steer axle can lead to a "heavy steering" feel and may cause the truck to react improperly to steering inputs
- Not enough weight on your steer axle can lead to a loss of traction for your steer tires
- Improper weight balance between your tractor drive tires and trailer tandems can lead to poor traction and an increased risk of jackknifing
- Too much weight toward the back of the trailer can lead to a "pendulum effect", causing the rear of the trailer to sway back and forth while driving down the highway or jackknife going around a curve
- Overloading a tire beyond it's maximum tire load capacity can cause tire damage and blowouts
- Overloading the suspension system of the truck can cause damage to the suspension system which could easily lead to loss of control of the vehicle
So as you can see, it's critical in so many ways to make sure that we follow the weight limits in strict accordance with the law. It is incredibly dangerous to overload a vehicle or to have the weight improperly distributed across the axles.
Methods Of Weight Transfer
There are several ways to distribute the overall weight of the vehicle across the different sets of axles. You will affect weight distribution by:
- Changing the weight distribution of the cargo along the length of the trailer, or moving the cargo around after loading the truth. This will distribute the weight mainly between your drive axles and trailer tandems
- Sliding your trailer tandems forward or backward will redistribute the weight mainly between your drive axles and trailer tandems
- Sliding your 5th wheel will redistribute the weight mainly between your steer axle and your drive axles
- Adding or burning off fuel will mainly change the amount of weight on your steer axle and somewhat on your drive axles also, depending upon the placement of your fuel tanks.
Limitations On Weight Transfer
There are several factors that will reduce the amount of weight we can transfer between the different sets of axles on the truck:
- Federal laws limit the maximum weight on any set of axles and the gross vehicle weight - 20,000 pounds single axle, 34,000 pound tandem axles, 80,000 pounds GVW
- The bridge law formula limits the maximum amount of weight you can carry across any set of axles based upon the number of axles and the spacing between them (we'll discuss this formula soon).
- The maximum legal length allowed between your trailer kingpin and your trailer tandems will limit how far back you can slide your tandems
- The load rating of the tires you have will determine the maximum amount of weight allowed on any particular tire
- The load rating of the suspension system will limit the amount of weight you can have on any axle
The Bridge Formula
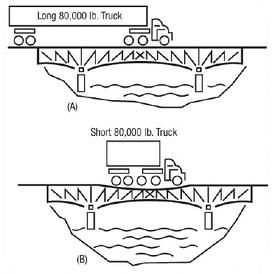
Congress enacted the Bridge Formula in 1975 to limit the weight-to-length ratio of a vehicle crossing a bridge. They accomplished this either by spreading weight over additional axles or by increasing the distance between axles.
The idea here was to prevent putting too much weight on a relatively small area, causing damage to the road surface and bridge structure. By requiring trucks to spread the weight across a longer distance and distributing the weight across more axles, you help prevent damage to the bridges and roadways.
Compliance with Bridge Formula weight limits is determined by using the following formula:
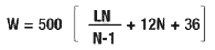
W = the overall gross weight on any group of two or more consecutive axles to the nearest 500 pounds.
L = the distance in feet between the outer axles of any group of two or more consecutive axles.
N = the number of axles in the group under consideration.
Altering The Weight Distribution
The primary factors which will affect the weight distribution across a truck's axles are:
- The position of the trailer's tandems
- The position of the tractor's 5th wheel
- The overall weight of the cargo in the trailer and the horizontal (front-to-back) position of its center of gravity
- The amount of fuel onboard and the placement of the fuel tanks
In the coming pages, we'll go through these one at a time and learn to apply each one individually. Later we'll put them all together and show you how to get your truck's weight distribution legal out on the highways, coast to coast, under any circumstances.




 TT On Facebook
TT On Facebook