Note: Your are not logged in. We can not keep your scores or track your progress unless you Register and Log In
SECTION 2: GENERAL PROVISIONS AND REQUIREMENTS (continued)
CATEGORY 3, cont.
Securement Devices, Assemblies and Components - Tiedowns:
A tiedown is made up of a combination of securing devices (that is, an assembly) that restrains cargo on a trailer (or vehicle), and that is attached to anchor points.
There are two types of tiedowns that are used to restrain cargo:
- Direct Tiedowns
- Indirect Tiedowns
Direct Tiedowns
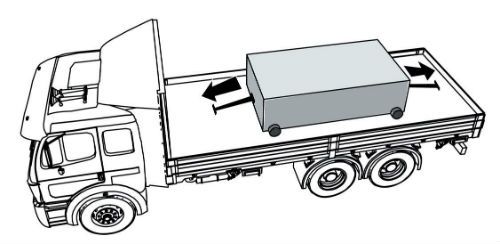
Direct tiedowns provide direct resistance to oppose the forces that are acting on the cargo. This direct resistance keeps the cargo in place, and prevents movement.
Indirect Tiedowns
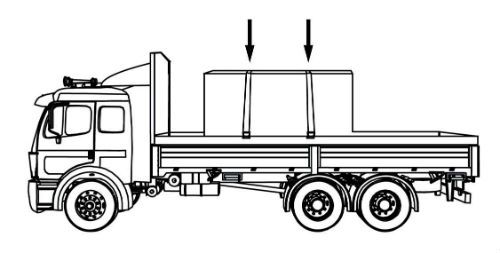
Indirect tiedowns create a downward force that increases the friction between the cargo and the deck. This increased friction restrains the cargo.
Responsibility for Tightening Tiedowns:
Tiedowns (except for steel strapping) must be designed, constructed and maintained so they can be tightened by the driver. Each tiedown must be attached and secured so it does not become loose or unfastened while the vehicle is in transit.
Location of Tiedowns:
All tiedown parts must be within the rub rails for platform type vehicles (this does not apply when the load extends beyond the rub rails).
Use of Edge Protection:

Edge protection must be used if a tiedown may be cut or worn. The edge protection itself must also resist crushing, cutting and abrasion. An edge protection device should fit properly on the edge of the article, with no space under the device for it to crush into.
CATEGORY 4
Dunnage Materials:
Timber used between tiedowns and cargo must be strong enough not to split or be crushed.
Any timber used should be properly seasoned, and free of rot or decay.
The grain should run lengthwise along the timber when it is used for structural purposes like blocking and bracing.
Timber should be free of knots, knotholes and splits that may affect its strength or interfere with nailing.
General Securement Requirements - Securement Options:
All types of cargo must satisfy one of the following three conditions when being secured:
- Fully contained by structures of adequate strength, or
- immobilized by structures of adequate strength to prevent shifting or tipping, or
- immobilized on or within a vehicle by appropriate means to prevent shifting or tipping.
Note: If additional securement is required for a specific commodity (such as metal coils), the specific requirements for securing that commodity take precedence.
Working Load Limit:
The Working Load Limit is the maximum load that may be applied to a component of a cargo securement system during normal service.
This value is assigned by the component manufacturer or the default rating in the Working Load Limit Table.
Note: Welded steel chain that is not marked or labeled with a grade or working load limit, is considered to have a working load limit equal to that for grade 30 proof coil chain.
 Cargo Securement Terms That Truck Drivers Should Know:
Cargo Securement Terms That Truck Drivers Should Know:
-
Deck:
The load carrying area of a truck, trailer, or intermodal container.
-
Void Filler:
Material used to fill a void between articles of cargo and the structure of the vehicle that has sufficient strength to prevent movement of the articles of cargo.
-
Cleat:
A short piece of material, usually wood, nailed to the deck to reinforce blocking.
-
Chock:
A tapered or wedge-shaped piece used to secure round articles against rolling.
Multiple-Choice Questions:
Cargo must satisfy one of the following securement conditions except:
- Immobilized by structures of adequate strength to prevent shifting or tipping
- Fully covered by a tarp.
- Fully contained by structures of adequate strength.
- Immobilized on or within a vehicle by appropriate means to prevent shifting or tipping.
All types of cargo must satisfy one of the following three conditions when being secured:
- Fully contained by structures of adequate strength, or
- immobilized by structures of adequate strength to prevent shifting or tipping, or
- immobilized on or within a vehicle by appropriate means to prevent shifting or tipping.
A chock is generally used to secure:
- Over-sized loads.
- Slippery articles.
- Round articles.
- Tall cargo.
Chock:
A tapered or wedge-shaped piece used to secure round articles against rolling.
Indirect tiedowns create what direction of force?
- Frontwards.
- Side-to-side.
- Backwards.
- Downward.
Indirect Tiedowns

Indirect tiedowns create a downward force that increases the friction between the cargo and the deck. This increased friction restrains the cargo.
A cleat is a short piece of wood used:
- To make pallets.
- To set cargo on top of.
- To fill empty space between cargo.
- To reinforce blocking.
Cleat:
A short piece of material, usually wood, nailed to the deck to reinforce blocking.
Timber used for dunnage must be all of the following except:
- Have grain should run lengthwise along the timber when it is used for structural purposes like blocking and bracing.
- Free of knots, knotholes and splits that may affect its strength or interfere with nailing.
- Properly seasoned, and free of rot or decay.
- All of these apply.
Timber used between tiedowns and cargo must be strong enough not to split or be crushed.
Any timber used should be properly seasoned, and free of rot or decay.
The grain should run lengthwise along the timber when it is used for structural purposes like blocking and bracing.
Timber should be free of knots, knotholes and splits that may affect its strength or interfere with nailing.
Void filler is:
- A tapered piece of material, thick at one end and thin at the other, used to help keep cargo from moving.
- A structure, device, or another substantial article placed against an article to prevent it from tipping that may also prevent it from shifting.
- A device placed between the deck of a vehicle and car or between articles of cargo, intended to provide greater friction than exists naturally between these surfaces.
- Material used to fill a void between articles of cargo and the structure of the vehicle that has sufficient strength to prevent movement of the articles of cargo.
Void Filler:
Material used to fill a void between articles of cargo and the structure of the vehicle that has sufficient strength to prevent movement of the articles of cargo.
In cargo securement, the deck is:
- A vertical barrier placed directly behind the cab of a tractor to protect the cab in the event cargo should shift forward.
- Part of the structure, fitting, or attachment on a vehicle or cargo to which a tiedown is attached.
- A rail along the side of a vehicle that protects the side of the vehicle from impacts.
- The load carrying area of a truck, trailer, or intermodal container.
Deck:
The load carrying area of a truck, trailer, or intermodal container.
Complete!
You can Return To The Table Of Contents




 TT On Facebook
TT On Facebook